While clinical diagnosis continues to grow increasingly accurate, the chances of STIs and UTIs being misdiagnosed, or mistaken for one another, is still worryingly high. That raises one very important question – why? Longevity Live Paid Partnership.
Awareness and knowledge of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and urinary tract infections (UTIs) are now higher than it ever has been. This is likely because conversations about sex and our sexual health are becoming much easier and less taboo – even if improvements still need to be made across the board.
However, despite this increase in awareness, the fact remains that both STIs and UTIs are regularly misdiagnosed by medical professionals. This can present a potential threat to someone’s physical and mental health, as well as anyone else they have sexual contact with. This can be made worse when someone is also unaware of their rights with regard to malpractice, such as the clinical negligence limitation period.
So, what causes STIs and UTIs to be misdiagnosed? That’s exactly what we’ll be taking a closer look at in the following post, so be sure to read on…

Photo by Womanizer Toys on Unsplash
What Is An STI?
An STI is an infection passed from one person to another through sexual contact. They are also often referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Some STIs can be treated and cured, while other more serious STIs cannot be cured.
An STI can affect anyone and are much more common than people initially expect. In the UK alone, over 460,000 STIs were officially diagnosed in 2019.
The most common way an STI can spread from one person to another is through unprotected (without a condom) vaginal, oral, or anal sex. An STI may also spread through genital touching. The symptoms of an STI can vary depending on the type of infection and, in some instances, there may be no symptoms at all. That being said, the most common symptoms are often:
- Discharge from the vagina, penis, or anus
- Pain while urinating
- Lumps or bumps
- Rashes
- Persisting itching
Common types of STIs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and genital warts.
What Is A UTI?
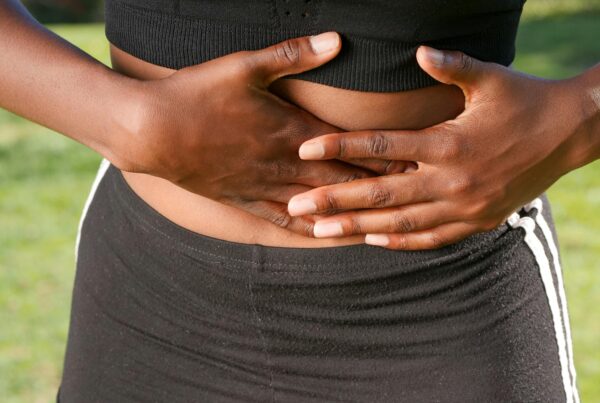
A UTI is an infection in any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The majority of infections involve the bladder and urethra. UTIs occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract and begin to multiply in the bladder. One of the most common causes of a UTI is sex.
UTIs are much more likely to affect women than men for a variety of reasons. The most notable being that women have a much shorter urethra than men. This bacteria is much more likely to reach the bladder. Symptoms tend to include pain when urinating, a constant urge to urinate, having blood in your urine, or pain in the tummy.
What Causes STIs and UTIs To Be Misdiagnosed?
Symptoms Are Similar Across The Board
One of the most common reasons for misdiagnosis of STIs and UTIs is that the symptoms are often so similar, doctors may mistake one for the other. For example, a burning sensation when urinating is one of the most common symptoms of both chlamydia and a UTI. This means it can often be difficult to tell the two apart – particularly if there are no other present symptoms.
Having An STI Will Result In A Positive UTI Test
One of the biggest issues that medical professionals need to navigate is the fact that women almost always test positive for UTIs when they give a urine sample. This is because the urine will be contaminated by normal bacteria that live in the vagina.
Doctors will then recommend treating the ‘UTI’ to avoid the potential worsening of infection, despite this not being the right approach.
Waiting Times Increase The Potential For Human Error
When testing for an STI, patients usually have to provide a urine or blood sample. This is then sent off for analysis, with the results then returning at a later date.
The fact that results don’t come back immediately presents a logistical issue that could cause misdiagnosis. Because results are likely to be handled by multiple people and travel between different labs, the risk of human error is always at play, which could affect the accuracy of a result or, in the worst-case scenarios, present a false negative.
An Increase In-Home Testing Increases Chances Of Misdiagnosis
Home testing for STIs and UTIs has become a very popular choice in recent years as it means people can complete tests in privacy. However, there are a couple of potential issues with this approach.
For one, the testing kits that are used from home may not be as accurate as ones that are provided in a hospital or doctor’s surgery. While the potential for human error when transporting these kits is another issue that needs to be resolved.

Photo by National Cancer Institute on Unsplash
Is There A Gender Imbalance In Diagnosing STIs and UTIs?
In many ways, there is an imbalance when it comes to diagnosing STIs and UTIs between men and women.
On the one side, STIs are often diagnosed much more accurately among men than they are women. This is because some of the symptoms of STIs, such as discharge, are much more obvious and are the reason a man will head to receive medical advice.
However, UTIs are much more likely to be misdiagnosed among men than they are women, simply due to the fact that they are much less common. Although they are one of the most common infections in women, just 3 percent of men worldwide are affected by UTIs each year.
Are You Concerned About An STI Or UTI Misdiagnosis?
In this post, we’ve discussed the difference between STIs and UTIs, as well as taking a look at why they may end up being misdiagnosed or mistaken for one another.
Have you ever received a misdiagnosis for an STI or UTI? Or do you have any other concerns about either condition? If so, feel free to leave a comment with your thoughts below.
Please be advised that this article is for general informational purposes only, and should not be used as a substitute for advice from a trained medical professional. Be sure to consult a medical professional or healthcare provider if you’re seeking medical advice, diagnoses, or treatment. We are not liable for risks or issues associated with using or acting upon the information on this site.







![women [longevity live]](https://longevitylive.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/photo-of-women-walking-down-the-street-1116984-100x100.jpg)