Did you know that losing weight has got to do with not only what you eat, but also how that food is broken down inside your body and, later, expelled? In a nutshell, your digestive system helps to utilize nutrients more effectively, which aids in weight loss. But there’s more…
What is digestion?
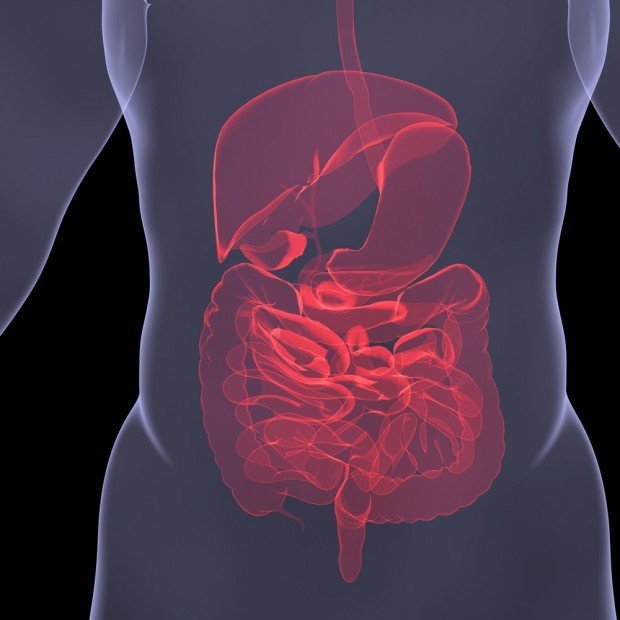
Without delving into a science lesson, the digestive system is made up of the gastrointestinal tract (which includes the stomach and intestines), the liver, the pancreas, and the gallbladder. Together with gut bacteria, hormones, and nerves, the digestive system’s organs break down the food and drinks we consume each day.
This broken-down food is used for energy, growth, and repair. Whatever is not used by the body is then expelled later that day.
So, how does digestion affect weight loss?
The role of the digestive system in weight loss
Digestion burns calories
The actual act of digesting food and liquids burns approximately 10% of the calories consumed.
It can slow (or speed up) your metabolism
Large quantities of gluten and starch (or simple carbs) are super easy for your body to break down, which slows the metabolism, leading to potential weight gain.
Protein, on the other hand, speeds up the metabolism. This increase in metabolism is known as the thermic effect of food.
Certain foods keep you fuller for longer
High-fiber foods take longer to digest, keep you full and satiated for longer, take away the craving to snack, and keep hunger at bay.
Food intolerances
Food intolerances (dairy and gluten being the most common) are a result of the body not being able to digest certain foods properly. This can leave you feeling bloated and suffering from stomach cramps and diarrhea.
A bout of severe diarrhea means the body won’t be able to absorb the nutrients it needs and puts the digestive system under stress. And a stressed system will go into “lockdown” and will store fluid and wreak havoc with our hormone levels, putting the whole digestive system out of whack, resulting in weight gain.
Leaky gut syndrome
Otherwise known as increased intestinal permeability, a leaky gut occurs when the barriers in the small intestines don’t work properly. These barriers (or gates) are there to let material/particles through into the bloodstream and to prevent harmful substances from getting in.
If these barriers let the unwanted substances into the bloodstream, this triggers the immune system, which leads to an imbalance of microbes in the gut, nutrition deficiencies, and food sensitivities, all of which can lead to weight gain.
Gut bacteria
Trillions of bacteria can be found in your intestines. They assist with digestion, your feeling of satiety, and how fat is stored – to name a few – all of which affect weight loss and gain.

SizeSquares/Shutterstock
Antibiotics, sweeteners, and preservatives kill off the good bacteria, paving the way for bad bacteria to thrive, which again, knocks your digestive system out of sync.
Symptoms of poor digestion
- Bloating
- Upset stomach
- Constipation
- Stomach cramps
- Heartburn
- Gas and burping
- Unwanted weight gain or weight loss
- Low libido
- Frequent yeast infections
- Brain fog
- Fortunately, you can break the cycle and get your digestive system back on track.
Tips to improve digestion
Keep a food diary to identify any food intolerances you may have and eliminate food from your diet accordingly.
Eat slowly
Gulping your food down puts stress on the digestive system.
Stay hydrated
Water keeps things moving, and it helps curb your appetite.
Eat fiber-rich foods
Fiber assists with keeping you full and keeps your digestive system operating smoothly.
Avoid excessive sugar and alcohol
Both can mess with your digestive system, so limit them as much as possible.
Choose ‘real’ food
Processed foods are harder to digest thanks to their high sugar and fat content. Eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, yogurt, and whole grains – the superfoods of good gut health!
Eat foods high in probiotics
Yogurt, sauerkraut, kimchi, kombucha. Probiotics maintain a healthy balance of bacteria, which helps the body with digestion and helps fight off the bad bacteria.
Get moving
Regular exercise keeps the food moving through your digestive system and helps with maintaining a healthy weight, which in turn promotes a healthy digestive system.
Relieve stress
Studies have shown stress plays a major role in digestion and digestive issues. Engage in regular stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or listening to calming music.
Take a supplement
Supplements can support gut health, assisting with the absorption of nutrients, as well as maintaining a healthy digestive tract.
Who is the author?

Kirsten Curtis
Kirsten Curtis is a freelance writer and editor who writes about health and wellness for Herbex Health. Her writing and editing career has had her cover a diverse range of topics over the years, from running and cycling to education, access control solutions, social development initiatives, and more.





![women [longevity live]](https://longevitylive.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/photo-of-women-walking-down-the-street-1116984-100x100.jpg)