Ultrasound technology has been around for many years. And over the years, it has become an essential tool in modern medicine.
In this post, we’ll explore the basics of ultrasound, some recent developments, the differences between the three key types of ultrasounds, and the risks involved. Longevity Live Paid Content.
What is an ultrasound?
Fundamentally, an ultrasound is a type of non-invasive medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal structures within the body. It’s widely used to diagnose and monitor a variety of medical conditions, including pregnancy, cancer, heart disease, and more.
During an ultrasound procedure, a transducer (a small handheld device) is placed on the skin, which emits sound waves. These sound waves bounce off the internal structures of the body and are then detected by the same device. They are then converted into images that a sonologist views on the monitor.
Uses of Ultrasounds
Ultrasounds are commonly used during pregnancy to monitor the development of the fetus and to check for any potential complications. They can also be used to diagnose a variety of medical conditions, such as:
- Gallstones
- Kidney stones
- Liver disease
- Thyroid problems
Ultrasounds can also be used to guide biopsies or other medical procedures, such as the insertion of catheters or stents.
In addition, ultrasounds are widely used in cardiology to diagnose and monitor heart disease. Echocardiography is a specialized type of ultrasound that uses sound waves to create images of the heart. This technology can provide detailed information about the structure and function of the heart, including the size and thickness of the heart’s walls, the movement of the heart valves, and the flow of blood through the heart. Ultrasounds are also used in diagnostic radiology to diagnose and monitor a variety of medical conditions, such as cancer.
Ultrasound-guided biopsies are often used to obtain tissue samples from tumors, and ultrasounds can be used to monitor the progression of cancer and to assess the effectiveness of treatment.
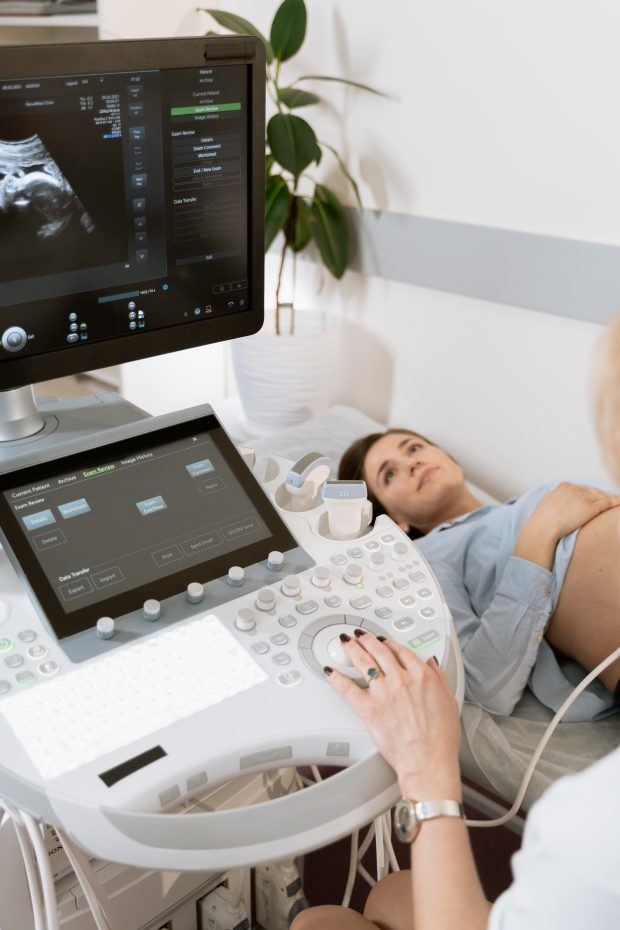
Photo by MART PRODUCTION
Types of Ultrasounds
Currently, there are three types of ultrasounds offered by medical facilities all around the world. These are:
2D Ultrasound Scans
2D ultrasound scans are the most commonly used type of ultrasound scan. They produce two-dimensional images of the inside of the body, providing doctors with valuable information about the size, shape, and structure of internal organs. These scans are widely used in obstetrics and gynecology to monitor fetal development during pregnancy. They are also used in other medical fields to visualize internal organs like the liver, kidneys, and bladder.
3D Ultrasound Scans
3D ultrasound scans provide a more detailed and realistic image of the inside of the body by creating a 3D image from multiple 2D images. Unlike 2D ultrasound scans, which provide a flat image, 3D ultrasound scans allow doctors to see the shape, depth, and texture of internal organs. It is commonly used in obstetrics and gynecology to provide detailed images of the developing fetus during pregnancy. They are also used in other medical fields to visualize internal organs and detect abnormalities like tumors.
4D Ultrasound Scans
4D ultrasound scans are similar to 3D ultrasound scans but provide the added dimension of time. These scans create a moving 3D image of the inside of the body, allowing doctors to see the movement and behavior of internal organs over time. 4D ultrasound scans are commonly used in obstetrics and gynecology to provide parents with a detailed view of their developing fetus during pregnancy. These are known as 4D baby scans. They are also used in other medical fields to visualize internal organs and detect abnormalities like tumors.
Differences between 2D Scan, 3D Scan, and 4D Scans
2D, 3D, and 4D ultrasound scans differ in the level of detail and complexity they provide. 2D ultrasound scans provide a flat, two-dimensional image of the inside of the body, while 3D ultrasound scans provide a more detailed, three-dimensional image. 4D ultrasound scans provide the added dimension of time, allowing doctors to see the movement and behavior of internal organs over time.
The three differ in terms of pricing and availability as well. 2D scans are the cheapest type of ultrasound varying from $50 – $100. These are followed by 3D scans, which cost $100 – $200. 4D scans have been the most expensive type of ultrasound. They can cost up to $500.
Also, 3D and 4D scans are available in a few medical facilities. These are not yet readily available at every other hospital.
Ultrasound Risks
Ultrasound scans are generally considered safe and non-invasive. However, there are some risks associated with their use, such as exposure to high-frequency sound waves, which can cause tissue heating and cavitation. Misdiagnosis is also possible if the ultrasound scan is not performed correctly or interpreted accurately. It’s important to note that 3D and 4D ultrasound scans should only be used for medical purposes and performed by trained professionals.
Final Thoughts
Summing up, ultrasound technology has greatly improved the accuracy and safety of medical diagnostics. Particularly, the use of 4D ultrasound scans has particularly revolutionized the field of obstetrics and gynecology.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated ultrasound scans that will provide more detailed and accurate information about the inside of the body. Hence, leading to improved medical outcomes and a better quality of life for patients.


![women [longevity live]](https://longevitylive.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/photo-of-women-walking-down-the-street-1116984-100x100.jpg)










