Nature has proven to be the source of many superfoods in various forms. Lion’s man mushroom is no different. However, it may be more than a mere source of nutrients.
Professor Frederic Meunier is from the Queensland University’s Brain Institute. In a recent study, he and his team claimed to have found new active compounds in the mushroom Hericium Erinaceus. Dr. Ramon Martinez-Marmol, the study’s co-author, said their intention was “to identify bioactive compounds from natural sources that could reach the brain and regulate the growth of neurons…” It seems as though that is precisely what they have done.
What Is The Lion’s Mane Mushroom?
Lion’s mane mushrooms – a.k.a Hericium erinaceus – is a mushroom that grows on trunks of dead hardwood trees, such as oak trees. This edible fungus has been used in East Asia, North America, and Europe. It has many culinary purposes and a long history of being used for its medicinal properties.
Scientific research has shown that lion’s mane mushrooms contain many health-promoting substances and beneficial plant compounds that impact the Central Nervous System. The compounds can:
- stimulate brain cell growth
- alleviate depression and anxiety
- support gut, heart, and immune health.
Professor Meunier says that he and his team have identified new active compounds from the mushroom. These compounds could help promote neurogenesis and enhance memories. Furthermore, it can treat and help prevent neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s.
How Does The Mushroom Work?
Lindsay Delk, RDN, specializes in the connection between food and mental health.
“Lion’s mane contains several compounds that may have beneficial effects on the body, including antioxidants, anti-inflammatory agents, and nerve growth factors.”
The mushroom is made up of active “ingredients”. The ingredients “help protect the body from damage caused by free radicals and inflammation,” thus aiding the promotion of nerve cell growth and regeneration. This is very important in the fight against neurodegenerative conditions. As they occur when nerve cells lose function over time and ultimately die.
Protection Against Neurodegenerative Conditions
The brain’s ability to grow and form new connections declines with age. This is why mental functioning worsens in those of older ages. Studies have found that the Lion’s Mane Mushroom contains compounds that can stimulate the growth of brain cells. Monique Richar is a registered dietician and nutritionist in Johnson City, Tennessee. She is also a spokesperson for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. According to her, lion’s mane has been linked with stimulating two key proteins: Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF).
Lion’s Mane Mushroom and Neurodegenerative Disorders
NGF is essential for the normal functioning of the Basal Forebrain, the part of the brain that produces acetylcholine, one of the most common neurotransmitters that brain cells use to transmit information. BDNF is vital in promoting neurons’ growth, repair, and normal functioning.
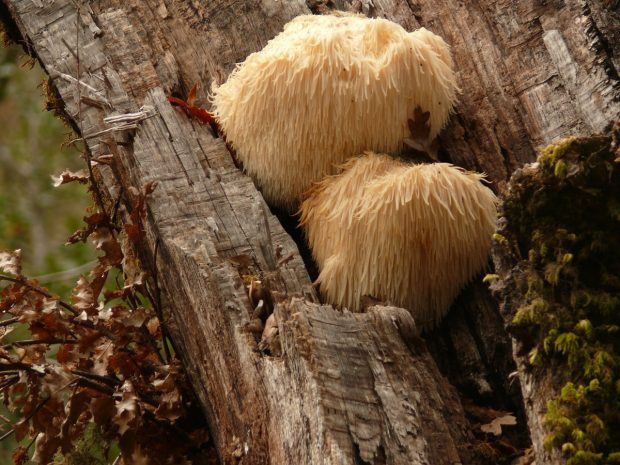

Chemicals such as hericenones and erinacines (which are present in lion’s mane mushrooms) stimulate the growth of these brain cells. Being present in the mushroom, it can therefore play a role in protecting the brain against neurodegenerative conditions, including:
- Alzheimer’s Disease: According to the Alzheimer’s Disease Association, about 6.2 million people are affected by Alzheimer’s. In a 2020 study, people aged 50 and older with mild Alzheimer’s disease symptoms showed significantly improved cognitive function after taking three 350 mg lion’s mane capsules daily for 49 weeks. Also, in another study, 77 people who had taken three 400 mg capsules daily for eight weeks had helped relieve depression, anxiety, and sleep disorders.
Lion’s Mane thus plays a critical role in neuroplasticity. This is the generation of new neural pathways in the brain following injury or illness. It is also an excellent source of neurotrophic compounds. This is a family of primarily protein-based biomolecules. These biomolecules promote the growth, survival, and healthy psychological function of both new and mature neurons. Also, these neurons are essential in regulating inflammation in the nervous system.
Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties
Many health conditions, such as heart disease and autoimmune disorders like arthritis, are due to chronic inflammation. Lion’s Mane mushrooms are rich in a specific type of carbohydrate called oligosaccharides, which have many critical biological functions. Including antitumor and antioxidative activities. They also exhibit immune-stimulating functions, which work together to lower the inflammatory fallout of various health conditions, including:
- Heart disease
- Liver damage
- Stroke
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Nervous System Injury Recovery
Consisting of the brain, spinal cord, and other nerves which travel throughout the body, the nervous system is composed of elements that work together to send and transmit signals. These signals are responsible for nearly every bodily function. A nerve injury can therefore be hazardous. It can affect the brain’s ability to communicate with organs and muscles. A nerve injury can affect the following three nerve groups, namely:
- Motor Nerves: Responsible for regulating all muscles under your conscious control. Damage to these nerves causes muscle weakness, painful cramps, and uncontrollable muscle twitching.
- Sensory Nerves: Responsible for relaying touch, pain, and temperature information. Damage to these nerves causes numbness and tingling in the hands and feet, trouble sensing temperature changes, and keeping your eyes closed. Components
- Autonomic Nerves: Responsible for regulating activities that aren’t consciously controlled, such as breathing, heart and thyroid function, and the digestion of food. Damage to these nerves causes excessive sweating, the inability to tolerate heat, gastrointestinal symptoms, and changes in blood pressure.
These injuries can cause paralysis and a loss of mental functions, which can take a long time to heal. However, research has shown that the lion’s mane mushroom can help speed recovery by stimulating the growth and repair of nerve cells.
How To Incorporate It Into Your Life
You can implement Lion’s Mane mushrooms into your diet by preparing them like ordinary mushrooms, as they are rather tasty and typical in cuisine. However, it is also available in supplement form, from powders and capsules to liquid extracts, such as:
Om Mushroom Superfood Lion’s Mane Organic Mushroom Powder
Dr. Emil Nutrition Lion’s Mane
A Superfood You Should Be Using
Lion’s Mane is a truly versatile superfood. It can contribute protein, vitamins, minerals, and complex carbohydrates to one’s diet. Regular use of the lion’s mane can help your body function effectively. It will also help maintain equilibrium in the presence of internal and external stressors.
So whether you’re adding it to your dinner table or scooping it into your workout smoothie, this can yield multiple health benefits. However, just like everything else, these supplements can carry side effects, including:
- Abdominal Discomfort
- Nausea
- Skin rashes
- Negatively interacting with blood-clotting medications
Additionally, researchers have conducted most tests on animals. As such, you must consult your doctor before implementing it into your lifestyle to ensure it doesn’t cause any adverse effects.
MAIN IMAGE CREDIT: stu_spivack/Flickr
References
- Cortonesi, P.M.M., de Almeida, L.F., Pinheiro, R.M.T., Périco, C.D.A.M. and Castaldelli-Maia, J.M., 2023. Use of Hericium erinaceus as a potential therapeutic of mental disorders: a systematic review. Debates em Psiquiatria, 13, pp.1-13.
- Ghosh, S., Nandi, S., Banerjee, A., Sarkar, S., Chakraborty, N. and Acharya, K., 2021. Prospecting medicinal properties of Lion’s mane mushroom. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 45(8), p.e13833.





![women [longevity live]](https://longevitylive.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/photo-of-women-walking-down-the-street-1116984-100x100.jpg)