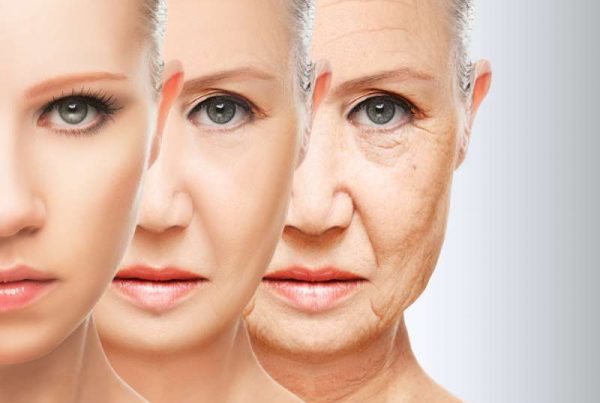
We may not have the complete secret to longevity. However, we do know some of the ingredients, one of which is diet. The foods we eat can have a profound effect on our health. In fact, some foods can even speed up, as well as slow down, aging.
So which foods can help us age better? Well, according to a recent study, certain foods may help to promote healthy aging.
Diet and Healthy Aging
A study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that “higher diet quality is associated with decelerated epigenetic aging.”

Evgeny Atamanenko/Shutterstock
What is epigenetic aging?
According to the Centers for Disease Prevention and Control (CDC), epigenetics refers to the study of how behavioral and environmental factors can trigger changes that affect the way our genes work (1).
DNA methylation is an epigenetic mechanism that helps to control gene expression – in fact, a previous study found that DNA methylation and epigenetic alterations have been directly linked to longevity in a wide array of organisms.
That said, the 2021 study found that through the right foods and nutrients, we can modify DNA methylation patterns. This can then help to improve our health and promote longevity.
What’s the best diet to reduce epigenetic aging?
Those who followed a diet high in fruits, veggies, grains, and legumes had fewer epigenetic age acceleration markers. It should be mentioned that their diets were also low in processed foods and sugars. As we know, a diet of this kind provides antioxidants and nutrients, which is great for our health;

Photo by Louis Hansel on Unsplash
“This favorable relation between higher diet quality scores and epigenetic age deceleration may be related to reductions in oxidative and inflammatory stress”
Want to know more?
Blue Zones are regions of the world inhabited by some of the oldest and healthiest people on the planet. These communities are largely free of diseases. As such, it would be naive not to think that their dietary habits played a role. So, what can we learn from them, and how can we eat to 100?
References
Johnson, A. A., Akman, K., Calimport, S. R., Wuttke, D., Stolzing, A., & de Magalhães, J. P. (2012). The role of DNA methylation in aging, rejuvenation, and age-related disease. Rejuvenation research, 15(5), 483–494. https://doi.org/10.1089/rej.2012.1324
Kim, Y., Huan, T., Joehanes, R., McKeown, N. M., Horvath, S., Levy, D., & Ma, J. (2021). Higher diet quality relates to decelerated epigenetic aging. The American journal of clinical nutrition, nqab201. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqab201



![women [longevity live]](https://longevitylive.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/photo-of-women-walking-down-the-street-1116984-100x100.jpg)