Arthritis is a disease which causes painful inflammation and stiffness in the joints. It is an incurable condition of the joints but it can be effectively controlled using certain medications.
Before we discuss the different types of treatments available for arthritis, let’s understand the types of arthritis.
Types of Arthritis
There are more than hundred types of arthritis. The most common types of arthritis are:
1. Osteoarthritis
It occurs when cartilage on both ends of the bone ends. Knees, hands, hips, and spine joints are the most commonly affected joints due to osteoarthritis. Symptoms of osteoarthritis include joint pain during or after movement, stiffness in joints after some time of inactivity, loss of flexibility in joints, swollen joints, and joint creaking. Osteoarthritis can occur because of ageing. Factors that can increase the likelihood of osteoarthritis include obesity, joint injuries, genetics, and bone deformities.

2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
It is a chronic inflammatory disease that can cause inflammation, swelling, and pain in the joints. Rheumatoid Arthritis affects the lining of the joints resulting in swelling of the joints. It occurs when the immune system of a person attacks it’s own body tissues by mistake. Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include pain and swelling in more than one joint, stiffness in joints, symmetrical joint involvement, fatigue, unsteadiness while walking, and loss of appetite. Factors that can increase the likelihood of rheumatoid arthritis include smoking, environmental exposures (exposure to asbestos or silica), obesity, and genetics.
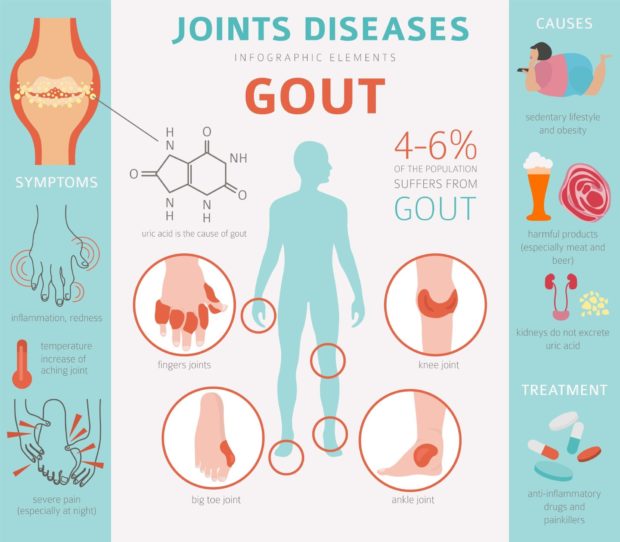
3. Gout
It is a type of arthritis that can cause intense pain, swelling, and stiffness in joints. Generally, it affects the joint in the big toe. It can also increase cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Gout is caused by excess uric acid in the blood. Gout attacks occur unexpectedly and they can harm tissues of the affected joint. Symptoms of gout are intense joint pain, lingering discomfort, inflammation and redness, and limited range of motion. Factors that can increase the likelihood of gout include lifestyle choices (high-purine diet or regular consumption of alcohol), genetics, obesity, and chronic lead exposure. According to Main Line Rheumatology, 4-6% of the population suffers from gout.
Now that we have understood what arthritis is and the common types of arthritis, let’s have a look at the treatments available for arthritis.
Best Treatments for Arthritis
There are lots of treatments available for arthritis but most of them have several side-effects such as hair loss, nausea, breathing difficulties, and increased blood sugar levels. If you want treatment with minimal side-effects, then CBD oil is the answer. CBD oil can be used to treat arthritis as it helps in reducing inflammation. CBD has a positive impact on the patient’s body as it decreases the sensations of pain without causing the common side-effects associated with usual treatments. As CBD doesn’t have any psychoactive properties, it can be used regularly without the feeling of being high.

Other treatments for arthritis include:
Medications
It depends on the type of arthritis present. Some of the commonly used arthritis medications are:
- Analgesics: It works as a pain reliever and doesn’t have any effect on inflammation. Examples of analgesics are acetaminophen (Tylenol), tramadol (Ultram), and Oxycodone (Percocet, Oxycontin).
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID): These drugs can reduce both pain and inflammation. NSAIDs can be taken orally as well as can be applied on joints (Topical use). Examples of NSAIDs are ibuprofen (Motrin IB, Advil) and naproxen sodium (Aleve). Side-effects of oral NSAIDs include stomach irritation, heart attack or stroke.
- Counterirritants: Creams or ointments that contain menthol or capsaicin, if rubbed over the skin of the joints can create a temporary hot sensation. These sensations affect the transmission of pain signals and distract the brain from the pain. Examples of counterirritants are eucalyptus, camphor, and wintergreen.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): These drugs stop the immune system from attacking the joints. Generally, it is used to treat Rheumatoid Arthritis. Examples of DMARDs are methotrexate and hydroxychloroquine.
- Biologic response modifiers: These drugs are genetically engineered drugs that target the molecules involved in the immune response. These drugs are typically used with DMARDs. Examples of biologic response modifiers are etanercept and infliximab.
- Corticosteroids: These drugs can be taken orally or can be injected directly into the joints. It reduces inflammation as well as decreases harmful autoimmune activities. Examples of Corticosteroids are Betamethasone, Cortisone acetate, and Dexamethasone.

Physical Therapy
Exercise can help in reducing some types of arthritis. It can improve the range of motion in the joints. However, exhausting exercises can worsen this condition, it is better to do low-impact exercises such as brisk walking, yoga, cycling and pilates. Regular exercise can take pressure off the joints.
Surgery
If medications, alternative treatments and physical therapy don’t help in reducing arthritis, then surgery may treat it. The common surgeries in this condition include:
- Joint repair: Joints can be realigned by joint repair surgery to reduce pain and improve function.
- Joint replacement: In this surgery, damage joints are completely replaced with an artificial one.
- Joint fusion: In this surgery, plates or rods are used to join two or more bones. This procedure is generally used for smaller joints such as ankles, wrists, thumbs, and spine.
- Osteotomy: This surgery involves the cutting of a bone to allow realignment or to shift the weight from an area damaged by arthritis to an undamaged area.
Final Words
With time, joint pain and stiffness can become very severe and may affect day to day activities of a person. It’s better to seek treatment if you have any of the above-mentioned symptoms to avoid risk in the long run. One of the best ways to prevent lifestyle diseases is to determine what your DNA makes you predisposed for. Click on the link to find out how a DNA test can help you to make the best preparations before disease hits.



![women [longevity live]](https://longevitylive.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/photo-of-women-walking-down-the-street-1116984-100x100.jpg)











Psoriatic arthritis that attacks the joints is an undetectable form of arthritis. If you have had eczema or psoriasis, and you test negative to osteo or rheumatoid arthritis, then you probably have psoriatic arthritis. This was my diagnosis by a rheumatologist last year who put me onto Methotrexate which I took once and decided not to take again (major side effects).
I have embarked on a journey trying to manage my pain via natural means. I have managed to reduce pain levels and may have found a way to relieve the pain levels even further.
Anyone is welcome to contact me.