Medical Research News Alert. New research from Advanced NanoBiomed Research shows testing a person’s blood can reveal the presence of circulating melanoma cells. This is an important breakthrough when it comes to managing skin cancer. A blood test will allow patients to forego invasive skin biopsies to determine whether they have skin cancer.
Why this blood test is important
Melanoma is one of the most aggressive cancers and it’s on the increase. There are over 300 000 new cases reported globally.
Early detection of melanoma is critical. Early stage localized melanoma patients have a 98% survival rate, while patients who develop metastatic melanoma can expect a 5–19% 5-year survival rate.
A blood test for skin cancer
Early detection of melanoma is not that simple. Up until now, it has been hampered due to the lack of promising markers for testing. This type of blood test will provide a more cost-effective and time-efficient diagnosis.
The blood test uses what’s called the Melanoma-specific OncoBean platform conjugated with melanoma-specific antibodies. Investigators at the University of Michigan showed that the test can be used not only to diagnose melanoma but also to evaluate whether all cancer cells have been successfully removed after skin cancer surgery.
A breakthrough
Researchers working on the project explain the breakthrough.
“This is the first comprehensive study of circulating tumor cells—or CTCs—to evaluate the efficacy of surgery using microfluidic systems in melanoma, including changes in the number of CTCs, CTC cluster configuration, and gene expression profiling,” said first author, Yoon-Tae Kang, PhD.
“CTCs have the potential to pinpoint treatment resistance and recurrence. They can be a valuable biomarker to non-invasively monitor for disease progression,” added corresponding author Sunitha Nagrath, Ph.D.
What you need to know about skin cancer
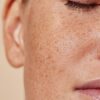
Skin cancer — the abnormal growth of skin cells — most often develops on skin exposed to the sun. However, it can also occur in areas of your skin not usually exposed to sunlight.
According to the American Cancer Society, skin cancer is by far the most common type of cancer. Nearly all skin cancers can be treated effectively if found early.
The risks associated with skin cancer
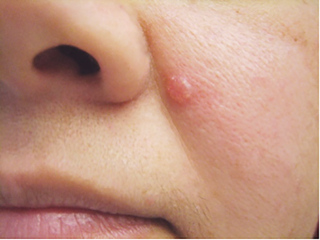
There are three major types of skin cancer — basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
According to the Mayo Clinic, “Skin cancer develops primarily in areas of sun-exposed skin, including the scalp, face, lips, ears, neck, chest, arms and hands, and in the legs of women. But it can also form in areas that rarely see the light of day. These include your palms, beneath your fingernails or toenails, and the genital area.”
Skin cancer affects people of all skin tones, including those with darker complexions. When melanoma occurs in people with dark skin tones, it’s more likely to occur in areas not normally exposed to the sun, such as the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. – Mayo Clinic
Reducing your risk
You can reduce your risk of skin cancer by limiting or avoiding exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Early detection of skin cancer gives you the greatest chance for successful skin cancer treatment.
If left untreated, this cancer can be potentially life-threatening. And that’s why it’s so important to see a doctor if you have any lumps, bumps, spots, sores, or other marks on your skin that are new or changing, or that worry you for any other reason.
A blood test, to help confirm or manage a diagnosis will go a long way to helping those at risk have better long-term outcomes.
References
Wiley Online Library: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anbr.202100083


![women [longevity live]](https://longevitylive.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/photo-of-women-walking-down-the-street-1116984-100x100.jpg)