Constipation is a medical term that represents a reduction in bowel movement or difficulty passing stool. While it technically depicts having fewer than three bowel movements a week, a person is considered to be constipated when a bowel movement results in the passage of small amounts of hard, dry stool. Affecting about 4 million people in the United States, constipation is considered the most common gastrointestinal complaint, resulting in about 2.5 million doctor visits annually.
Causes of Constipation
Constipation doesn’t have one single cause. Differing from person to person, the most common causes include:
1. Affected colon activity
The colon is the longest part of the large intestine. Its primary role is to absorb water from partially digested food as it passes through your digestive system. It then forms stool, which the colon muscles propel through the rectum to be passed out. If you’re constipated, it usually means food is moving too slowly through the digestive tract. This gives the colon too much time to absorb water from waste, making it dry, hard, and difficult to push out.
2. Lack of fiber in your diet
Research has shown a link between a low-fiber diet and an increased risk of constipation. Some researchers cite it as a leading cause. Fiber moves through the digestive system rather than getting broken down and absorbed, binding water and waste together, causing stool to be larger, softer, and easier to pass. Insoluble fiber also helps speed up food transit in your digestive system, which helps prevent constipation.
3. Lack of exercise
According to experts, exercise does more than tone muscles and aids heart health. The colon responds to physical activity, with good muscle tone being important for regular bowel movement. Exercise helps constipation by lowering the time it takes for food to move through the large intestine, limiting the amount of water the body absorbs from the stool. This helps ensure that it isn’t hard or dry.
4. Certain medications
A range of medications have been shown to increase your risk of constipation, including:
- Pain medication: Opioids slow down the movement of stools through your colon. This gives your colon more time to absorb water from the stool, causing it to become hard, dry, and difficult to pass out.
- Calcium-channel blockers: Typically used to relax muscles in blood vessels to lower blood pressure, one of their side effects is relaxing muscles in your gut, leading to constipation.
- Tricyclic antidepressants: Usually prescribed for depression, anxiety, or insomnia, these can cause constipation due to their anticholinergic effects. This means they block the effects of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that controls nerve endings in various body organs, including the digestive tract. When this is blocked, the muscular contractions responsible for propelling waste through the digestive tract are slowed, leading to a hard, dry stool.
5. Dehydration
As stool moves through the large intestine, the water is naturally absorbed. If your body doesn’t have enough fluids, the intestine removes extra water from the stool, which would typically be required for healthy waste removal.
6. Stress
Research seems to indicate a strong connection between the brain and the bowel. The same neurotransmitters that send signals to the nerves in the brain also affect bowel nerves. Stress can cause changes in the release of bowel neurotransmitters. These stress-related changes can directly impact your bowel function, resulting in constipation or diarrhea.
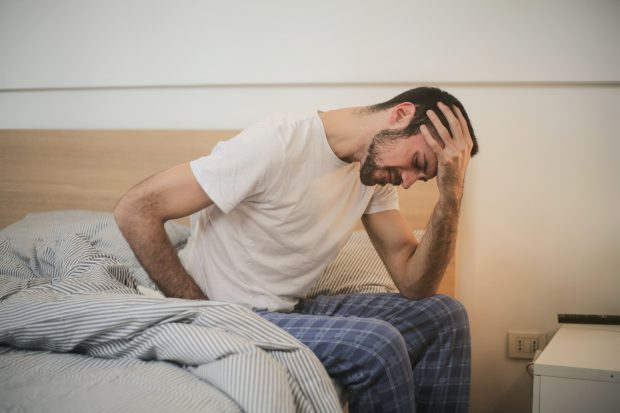

Photo by Andrea Picquadio on Pexels
Natural Remedies In Your Kitchen
Constipation can be very unpleasant and even debilitating in some instances. However, there are some natural remedies that you can find in your kitchen to help alleviate its intensity and related symptoms. These include:
1. Coffee
While coffee doesn’t have the same bowel-stimulating effect on everyone, research shows that coffee promotes the urge to poop in at least one-third of the population. Coffee contains acids that can boost gastrin levels.
Gastrin is a hormone shown to stimulate hydrochloric acid and digestive enzyme production in the stomach. Along with this, it increases stomach contractions and relaxes the sphincter between your stomach and small intestine. Patients with constipation demonstrate decreased gastrin levels, which coffee can fix.
2. Prunes
Prunes are quite high in sorbitol, having about 14.7g of sorbitol per 100g serving. Sorbitol is a naturally occurring fruit sugar alcohol that has been shown to be hyperosmotic, enabling it to act as a constipation reliever. If you’re not used to regularly consuming prunes, the sudden increase in sorbitol consumption can cause diarrhea.
Also, prunes are a source of both insoluble and soluble fiber. While insoluble fiber helps maintain regular bowel movement, soluble fiber helps moderate digestion. The high fiber and sorbitol content combination leads to a laxative effect on your body, which can be had in their normal form, or in prune juice form.
3. Yogurt
While all types of yogurt can help maintain a healthy digestive tract, yogurt with live cultures and probiotics can be an effective aid for constipation. Ongoing research has shown probiotics’ ability to improve digestion. A study showed that pregnant women experiencing constipation showed increased bowel movement after consuming 30g of probiotic yogurt enriched with bifidobacterium and lactobacillus bacteria.
However, it is important to note that consuming an excessive amount of probiotics can result in constipation, so moderation is key.
4. Olive oil and flaxseed
Olive oil can have mild laxative effects. The fats it contains can help smooth the inside of the bowel, making it easier for stools to pass. It also helps the stool hold in more water, which keeps it soft. Flaxseed is also effective in treating constipation as a source of soluble fiber. It dissolves in water, which makes the stool softer and easier to pass. While many opt for it in oil form, you can also consume it in its whole or ground seed form.
5. High fiber, high water fruits
A few high-fiber, high-water fruits that can help ease constipation include:
- Kiwifruit: 10g of kiwifruit can contain about 3g of fiber. It also contains actinidine, an enzyme that alleviates upper gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Apples and pears: As sources of fiber, sorbitol, and fructose, these fruits also contain high amounts of water, which can ease digestion and prevent constipation.
- Blackberries and raspberries: As rich sources of fiber and water, eating a handful of these fruits can also help ease constipation.
Should You Visit Your Doctor?
While most cases of acute constipation are due to lifestyle factors or diet, chronic constipation can also occur, signaling an underlying condition. These can include:
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Diabetes
- Hyperthyroidism
- Celiac disease
- Proctitis
If you suspect that you may be experiencing any of this, it’s best to visit your doctor. They not only determine what may be causing your constipation but also provide suitable remedies and treatments to enhance your bowel movements. These natural interventions are in no way designed to replace the medication or treatment your doctor advises.



![women [longevity live]](https://longevitylive.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/photo-of-women-walking-down-the-street-1116984-100x100.jpg)